- Coenzyme F420
-
Coenzyme F420 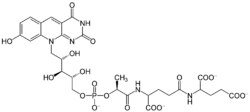
Structure de la coenzyme F420.Général No CAS PubChem ChEBI SMILES InChI Propriétés chimiques Formule brute C29H32N5O18P [Isomères] Masse molaire[1] 769,5608 ± 0,0318 g·mol-1
C 45,26 %, H 4,19 %, N 9,1 %, O 37,42 %, P 4,02 %,Unités du SI & CNTP, sauf indication contraire. La coenzyme F420, ou 8-hydroxy-5-déazaflavine, est une coenzyme flavinique intervenant dans les réactions d'oxydo-réduction chez les archées méthanogènes[2], chez de nombreuses actinobactéries, et ponctuellement chez d'autres lignées bactériennes. C'est un substrat pour la 5,10-méthylènetétrahydrométhanoptérine réductase et la méthylènetétrahydrométhanoptérine déshydrogénase[4],[5]. Cette coenzyme doit son nom à son maximum d'absorption à λmax = 420 nm.
Structurellement semblable à la riboflavine et au FAD, elle agit davantage comme la nicotinamide. Son potentiel d'oxydo-réduction vaut -350 mV, valeur proche de celle du NADH et du NADPH (-320 mV) ; comme ce dernier, F420 apporte un anion hydrure H-, composé d'un proton et de deux électrons.
Cette structure se retrouve chez les archées, mais aussi chez les bactéries Gram-positives telles que Streptomyces (actinomycètes) et Mycobacterium[6]. Des variantes de ce cofacteur ont également été identifiées chez une cyanobactérie, Anacystis nidulans[7] ainsi qu'une algue verte, Scenedesmus acutus, qui est un eucaryote.
F420 intervient dans les processus de méthanogenèse[8], de réduction des sulfites[9], la détoxination des dérivés réactifs de l'oxygène[10]et la chaîne respiratoire[11] chez les archées.
Une source particulièrement riche en F420 est Mycobacterium smegmatis, dans laquelle plusieurs dizaines d'enzymes utilisent du F420 comme cofacteur à la place de la FMN utilisée par les enzymes homologues de la plupart des autres espèces[12].
Sommaire
Notes et références
- Masse molaire calculée d’après Atomic weights of the elements 2007 sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- (en) Deppenmeier U, « Redox-driven proton translocation in methanogenic Archaea », dans Cell. Mol. Life Sci., vol. 59, no 9, 2002, p. 1513–33 [lien PMID, lien DOI]
- (en) Fox JA, Livingston DJ, Orme-Johnson WH, Walsh CT, « 8-Hydroxy-5-deazaflavin-reducing hydrogenase from Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum: 1. Purification and characterization », dans Biochemistry., vol. 26, no 14, 1987, p. 4219-4227 [lien PMID, lien DOI]
- (en) C. H. Hagemeier, S. Shima, R. K. Thauer, G. Bourenkov, H. D. Bartunik, U. Ermler, « Coenzyme F420-dependent methylenetetrahydromethanopterin dehydrogenase (Mtd) from Methanopyrus kandleri: a methanogenic enzyme with an unusual quarternary [sic] structure », dans J. Mol. Biol., vol. 332, no 5, 2003, p. 1047–1057 [lien PMID, lien DOI]
- (en) G. D. Vogels, C. Van Der Drift, J. T. Keltjens, W. J. Geerts, « Purification and properties of 5,10-methylenetetrahydromethanopterin dehydrogenase and 5,10-methylenetetrahydromethanopterin reductase, two coenzyme F420-dependent enzymes, from Methanosarcina barkeri », dans Biochim. Biophys. Acta., vol. 1079, no 3, 1991, p. 293-302 [lien PMID, lien DOI]
- (en) J. R. D. McCormick et George O. Morton, « Identity of cosynthetic factor I of Streptomyces aureofaciens and fragment FO from coenzyme F420 of Methanobacterium species », dans J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1982, 104 (14), 4014-4015. DOI:10.1021/ja00378a044
- (en) A. P. Eker et al., « DNA photoreactivating enzyme from the cyanobacterium Anacystis nidulans », dans J Biol Chem. 1990, 265 (14), 8009–8015.
- (en) D. E. Graham et R. H. White, « Elucidation of methanogenic coenzyme biosyntheses: from spectroscopy to genomics », dans Nat Prod Rep. 2002, 19 (2), 133–147.
- (en) E. F. Johnson et B. Mukhopadhyay, « A new type of sulfite reductase, a novel coenzyme F420-dependent enzyme, from the methanarchaeon Methanocaldococcus jannaschii », dans J Biol Chem. 2005, 280 (46), 38776-38786.
- (en) H. Seedorf et al., « F420H2 oxidase (FprA) from Methanobrevibacter arboriphilus, a coenzyme F420-dependent enzyme involved in O2 detoxification », dans Arch Microbiol. 2004, 182 (2-3), 126-137.
- (en) U. Deppenmeier, « The membrane-bound electron transport system of Methanosarcina species », dans J Bioenerg Biomembr., 2004, 36 (1), 55-64.
- (en) J. D. Selengut, D. H. Haft, « Unexpected abundance of coenzyme F(420)-dependent enzymes in Mycobacterium tuberculosis and other actinobacteria. », dans J Bacteriol., vol. 192, no 21, 2010, p. 5788-5798 [lien PMID, lien DOI]
Voir aussi
Articles connexes
Liens externes
Catégories :- Composé du phosphore
- Coenzyme
- Méthanogenèse
- Flavine
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
